Coconuts are actually not nuts – they are closer to peaches than walnuts
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(jpeg)/SEA-WhatisaCoconutHero-GettyImages-74ac96309ffb4d9f814134cb1903996b.jpg)
All over south India, Southeast Asia, the Pacific Islands, Caribbean, Africa and Latin America, coconuts are a staple. However, they are more than just eating – in places where coconuts are an essential harvest, have a meaning that goes beyond the culinary way. In many cultures, coconuts can have both spiritual importance as well as cultural importance and symbolize hospitality, tradition and more. The offer of a sophisticated coconut in India, for example, is a gesture of respect and blessing.
The coconut is also a versatile harvest. Various forms of edible “nut” are used in shells in many kitchens. But it’s not just a food source: the shells and fronds are used to produce ropes, networks and building materials. The trunk becomes the wood after the tree has listed the fruit. And the shells are transformed into carbon black (a kind of charcoal). In the Philippines, the versatility of the coconut tree brought him the name “Tree of Life”.
But what exactly is a coconut?
What is a coconut?
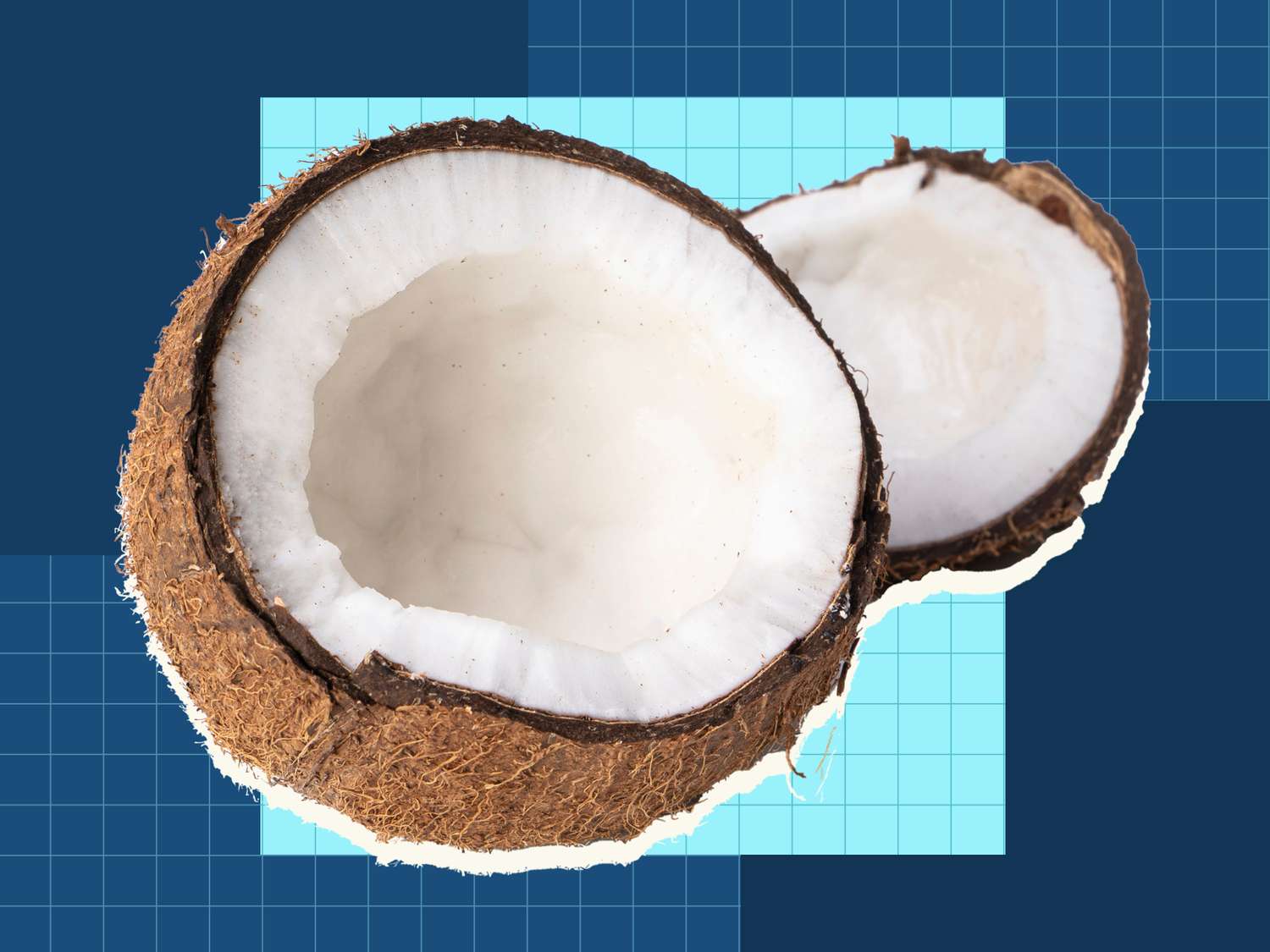
Botanical is a coconut of the seeds of a drupe and, in contrast to hazelnuts or walnuts, there is no real nut. “A drupe is a hard -plated fruit with a fleshy or fiber outer layer,” says Marc Hacadourian, director of Glasshouse Horticulture in the New York Botanical Garden. Further examples of switch are peaches, olives and almonds.
If you imagine a coconut, don’t start with the hairy brown ball – that’s just the mature seed. Instead, imagine coconuts how they appear when they are hacked open for fresh coconut water: large, green, smooth and slightly pointed or oval in shape. Here are the layers of this fruit:
- Exocarp: The smooth green or yellowish outer skin.
- Mesokarp: The thick, fibrous layer under the Exokarp, the cocus is called. It is inedible, but has many non-culinary uses, including rope, mat and fishing nets.
- Endokarp: The hard brown case with three “eyes” at one end contains the seed.
- Endosperm: The white meat and the liquid in the shell that feeds the germ, the embryo, which can sprout into a new tree.
If a coconut fruit is young (approximately six months old), the endosperm is mostly liquid-das nutrient-rich coconut water, which we all like to drink. When the fruits ripen, dissolved solids solidify in the water slowly, first in a soft jelly and then in solid white meat. After about a year, a coconut is mature, with thick meat and much less water.
Coconuts are usually divided into two categories based on age: young or ripe. According to Hacadourian, delicate young coconuts are harvested after five to seven months if they have soft meat and sweet water. Ripe coconuts, on the other hand, are 11 to 12 months old and have a thick, solid meat.
How to buy and store fresh coconuts
Fresh coconuts are not common in generic supermarkets, but many Asian or Caribbean grocery stores are wearing them.
How to buy for young coconuts: Young coconuts can be sold entirely with their green outer layer to reveal the white, fibrous shell. For the whole green coconut, check for freshness: the fruits should feel heavy and fluid when shaking. Avoid coconuts with mold, dark spots or cracks.
How to buy coconuts for mature: Similar to young coconuts, ripe coconuts should feel heavy and black when shaking, which shows freshness, since an old coconut does not have much water inside. Avoid a mold on the bowl or eyes. (If the opening of an intimidating appears, our guide is on How to open a coconut will make the process less discouraging.)
How to store young and mature coconuts: Refrocation you young coconuts. Store the water and meat in an airtight container for up to four days in the fridge or up to two months in the freezer. Unexpected mature coconuts can be kept at room temperature for up to three months. After opening the meat in an airtight container, cool up for up to four days or freeze for up to six months.
How and when to use fresh coconuts
Young coconuts: The young coconuts that are valued for their water and a jelly-like meat can be enjoyed directly from the case or used in smoothies and cocktails. The meat works well in desserts how how Philippines breakfast Pandan (Young coconut and pandan -gelee -pudding), Thai ittim gati (young cocose ice) or coconut -ceviche.
Mature coconuts: Fresh or thawed mature coconut meat can be used in SaucyPresent SoupChutney or vegetable sites. Furnished coconut meat can be mixed with water to make fresh Coconut milk. In southern India, crushed mature coconut is mixed with Jaggery and cardamom, filled into a rice flour and damped for sweet dumplings as “Sihi Kadubu” or “Kozhukatta”.
A list of common coconut products
Here you will find an overview of various coconut products and by -products that are usually sold in the USA.
Entire coconuts
Mature coconuts: Hardly shook, brown, hairy seeds with solid meat and some coconut water.
Young coconuts: Delicate, green coconuts filled with coconut water, sometimes sold with the green outer layer.
Both types can be difficult to open and are not widespread in generic US supermarkets.
Getty Images / Mariusfm77
Coconut milk
Coconut milk is manufactured by mixing mature coconut meat with water and then the mixture is tense. It is sold in boxes or cooled with other milk -free milk. To make it at home, mix chopped fresh coconut with water and strain them through a fine mesh sieve or a cheese cloth. The shelf-stable coconut milk is heated, homogenized and ultra-pasteurized and can be sweetened or unsweetened. Unpasteurized coconut milk must be cooled at any time.
Note: Do not mix coconut milk with coconut cream that contains more meat and less water.
How to use coconut milk: Use it to lend wealth CurryPresent riceOr desserts like banana (a Malaysian banana soup). When a can of coconut milk is separated into cream and water, stir together before use.
How to keep coconut milk: store unopened coconut milk in doses at room temperature. After opening, cool in an airtight container and use within five days. Cooled, non -pasted coconut milk should be consumed within seven to ten days after opening.
Serious food / Karina Matalon
Coconut oil
Coconut oil can be pressed hot or cold and is semi -colored at room temperature and when it is cooled.
- Hot pressed: Made by cooking coconut milk until the water evaporates and the oil remains.
- Cold pressed: Made by pressing coconut meat in a mechanical press to drive away the oil.
Coconut oil can be refined or not refined.
- Refined coconut oil is steamed, bleached and deodorized. This process according to A 2020 study Published in Efood“Deactivates the bioactive components such as Tocopherol and Polyphenols”, which are responsible for the nutty aroma of Coconut and create an oil with little taste or smell.
- Coconut oil without unnecessary (or virgin) coconut oil is typically cold pressed and preserved its coconut aroma.
Getty Images / Jayk7
Both types can be used for cooking, but refined oil has a higher smoke point and a neutral taste, which makes it better for highly heated applications such as the seafall and in every dish where you do not want to taste or smell the coconut yourself. Virgine’s coconut oil, on the other hand, gives a pleasant coconut aroma and a pleasant aroma, where it is also used.
How to use coconut oil: With its relatively high smoke point, coconut oil is well suited to SEND, roast, fry, sauté and fry. Melted, it can be replaced by rapeseed or vegetable oil when baking. It’s also great to make magic SleeveAdd to smoothies or poping Popcorn.
How to save coconut oil: Store in a cool, dry place.
Coconut sugar
Coconut sugar is produced by reducing the juice of the coconut palm flowers until most of the moisture has evaporated. The crystals are mahogany in color and slightly finer than granulated sugar. Coconut sugar, sometimes referred to as coconut palm sugar, should not be confused Palm sugar. Palm sugar, on the other hand, is a more general category of many different types of palm juice.
Getty Images / Domnicky
How to use coconut sugar: Replace it with granulated sugar when baking or cooking. Note that it adds a caramel -like taste.
How to save coconut sugar: Hold in an airtight container in a cool, dry place.
Coconut broken off, crushed and dried out
Coconut are made of dehydrated coconut meat, although coconut can also be found fresh and frozen. The coconut of flakes is long and wide and often sold as coconut chips. Crazy coconut is finer than the cut sibling, and the dry coconut is finely grated. All three are sweetened or unsweetened, roasted or up to be assigned.
How to use: Dried coconut appears in baked goods and desserts worldwide, including CakePresent MacaronAnd cake. It also has dishes like Filipino Blanca Maja (Coconut pudding) and Malaysian Where (Pandan adhesives with coconut), hearty Filipino Binakol (Chicken and coconut soup) and crispy Coconut shrimp.
How to save: Hold the dried coconut in an airtight container in a cool, dry place.
Getty Images / Lena_zajchikova
Freshly grated coconut meat
Freshly grated coconut meat is often sold frozen and retains a large part of its fresh taste and fresh texture as soon as they have been thawed. It has to be cooled and used within three to five days after thawing. Search for it in Asian or Caribbean grocery stores.
Take away
Coconuts are incredibly versatile. They can play fresh, dried or frozen and their many by -products – milk, oil, sugar and much more – play with roles in kitchens around the world.